This is the survival unit of the bank because until and unless the success of this department is attained, the survival is a question to every bank. If this section does not properly work the bank itself may become bankrupt. This is important because this is the earning unit of the bank. Banks are accepting deposits from the depositors in condition of providing interest to them as well as safe keeping their interest. Now the question may gradually arise how the bank will provide interest to the clients and the simple answer is – Loans & Advance.
Credit is continuous process. Recovery of one credit gives rise to another credit. In this process of revolving of funds, bank earns income in the form of interest. A bank can invest its fund in many ways. Bank makes loans and advances to traders, businessmen, and industrialists. Moreover nature of credit may differ in terms of security requirement, disbursement provision, terms and conditions etc. The bankers have to keep in mind that lending is for the best interest of the community and lending should be directed to productive sectors only.
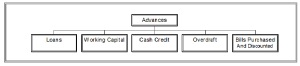
We often use loans and advances as an alternative to one another. But academically this concept is incorrect. Academically Advances is the combination such items where loans is a part only. For this credit section of the banks is known as advance section. Academically Advance is the combined form of the following items
Functions of Advance Department:
- Ensuring that funds are disbursed only after compliance with terms and conditions or required documents received.
- Make sure that the bank has always valid and current loan documentation.
- Ensuring that the collateral security is adequate at times to support the loans.
- Keeping the loan documentation under safe custody.
- Ensuring that the bank receives sufficient valid insurance cover whenever required from a recognized insurance company.
- Monitoring the receipt of periodical receivable.
- Debiting the client for all charges, interest etc.
- Maintaining the central liability records for all extensions of credit and balancing the totals with General Ledger.
- To earn interest from the borrowers and give the depositors interest.
- To accelerate economic development by providing different industrial as well as agricultural advances.
- To create employment by providing industrial loans.
- To pay the employees as well as meeting the interest groups.
Sound Principles of Lending, Credit Investigation and Selection of Borrowers
Introduction:
Lending involves elements of risks. The element of risk, in the main operations of a bank, leads to the necessity of credit investigation. It presupposes right selection of borrower, which needs complete and comprehensive investigation of all the facts. As a matter of fact, much of the worries of the lending banker is over if correct type borrowers can be selected. To arrive at a decision about selection of a borrower the banker needs to collect a long chain of information about the borrower. Usual loan application forms when filled in by the applicant provide the banker with almost all the required particulars pertaining to the advance. The banker’s responsibility is to verify and correlate those statements and to prepare a credit report, which is expected to give a complete, clear, correct and reliable record of the character, means and business integrity of the borrower. On the basis of credit information and credit report, the banker may arrive at a reasonably correct decision about the proposed advance. Credit investigation is, therefore, a sacred and obligatory job of a lending banker for administering his lending operations with success.
Sound Principles of Lending:
It is a fundamental precept of banking everywhere that advances are made to customers in reliance on his promise to repay, rather than the security held by the banker. Although all lending involves some degree of risks, it is necessary for any bank to develop sound and safe lending policies and new lending techniques in order to keep the risk to a minimum. As such, the banks are required to follow certain principles of sound lending.
Safety: Advances should be expected to come back in the normal course. The repayment of the loan depends upon the borrower’s capacity to pay and willingness to pay. The capacity depends upon the tangible assets of the borrower. The willingness to pay depends upon the honesty and character of the borrower.
Liquidity: Liquidity is the availability of bank funds on short notice. The borrower must be in a position to repay within a reasonable time. Liquidity also signifies that the assets should be salable without any loss.
Profitability: A banker has to see that major portion of the assets owned by it are not only liquid but also aim at earning a good profit. The difference between the interest received on advances and the interest paid on deposits constitutes a major portion of bank’s income. Besides, foreign exchange business is also highly remunerative.
Purpose: A banker would not throw away money for any purpose for which the borrower wants. The purpose should be productive so that the money not only remains safe but also provides a definite source repayment.
Security: Security serves as a safety valve for an unexpected emergency. The security offered for an advance is a cushion to fall back upon in case of need. An element of risk is always present in every advance however secured it might appear to be.
Spread/ Diversity: The advances should be as much broad-based as possible and must be in keeping with the deposit structure. The advances must not be in one particular direction or to one particular industry. Again, advances must not be granted in one area alone.
National Interest: Bank has significant role to play in the economic development of a country. The banker would lend if the purpose of the advance is for overall national development.
Credit Investigation:
Different phases of Credit Investigation:
- Collection of information of the entrepreneur
- Preparation and analysis of this information in order to determine creditworthiness of the borrower/ entrepreneur
- Making decisions and recommendations about the borrower
- Furnishing credit information to other bankers
- Retention of the information for future use
Sources of information for credit investigation:
- Personal Interview:
The first and most obvious information that can be derived from the borrower by personal interview in the following manner:
- Refreezing:
- Try to get introduced with the entrepreneur
- Be informal with him
- Know him personally and earn his acceptance
- Be frank, upright and sincere
- Assessing achievement need:
- Ask about his past experiences during student life and afterwards and try to assess whether he is a winner character or loser
- Mark his enthusiasm when the entrepreneur describes his achievement/ success
- Try to assess the extent of optimism and pessimism
- Make notional rating about his achievement need (positive/neutral/negative)
- Assessing attitudes of the entrepreneur:
- Try to note entrepreneur’s responses indicating his inclination to literature, business, economics, history etc.
- Check and recheck if his attitude is proper towards business management
- Examine his responses and deliberations to find out whether trend of response is positive or negative
- Try to assess his attitudes on the above lines and rank him accordingly (High/average/low)
- Assessing overall knowledge about the project:
- Discuss about the project the entrepreneur has submitted
- Check if he is familiar with the project that contained in the profile
- Check the information given by the entrepreneur contained in the profile
- Rank his project knowledge according to the correctness of project information (high/modest/low)
- Assessing management skill:
- Try to assess entrepreneur’s skills in managing people, material resources and financial resources
- Try to know his capability about assessing others
- Note if he is critical about others
- Note his appreciation about others
- Assess his knowledge about the product/service
- Assess his knowledge about the competitors
- Assess his knowledge about the price, consumer group and consumer behavior
- Assess his knowledge about actual market where his product is likely to be marketed
- Assess his knowledge about demand gap
- Rank his management skill on the basis of above discussion (high/average/low)
- Borrower’s Loan Application: Loan application entails a detailed questionnaire where from borrowers answer provide some basic information
- Bank’s own record: Bank’s own record provides applicant’s transaction behavior. In case of old borrower information are available regarding previous borrowings and the repayments were made as per sanction stipulation.
- Reports obtained through friends or rivals: Banks may obtain information about the borrowers in the same line of trade or business.
- Confidential Report/ Status Report from fellow bank
- Spot verification
- Market reports
- Financial statement of the applicant
- Income Tax statement
- Report from CIB
- Trade checking
- Reports from Chamber of Commerce and Industry
- Reports from Registrar of Joint Stock Company in case of Limited Company
- Personal visit to the applicant’s business, plant or trade center
- Other sources:
a). Press reports regarding purchase, sale, auction of property
b). Registration records, municipal records etc.
Preparation of Credit Report:
On the basis of credit investigation, bankers prepare a credit report for the applicant usually as per proforma used by the respective bank. The report generally includes the following under different ownership:
- Name
- Worth
- Date
- Registered Office
- Address (present, permanent and business)
- Nature of business
- Constitution of the firm
- Date of establishment
- Incorporation and Commencement certificate
- Associates and allied concerns with details of assets and liabilities
- Manufacturing and Trading Account
- Profit & Loss Account
- Analysis of Balance Sheet
- Facilities requested
- Ability to furnish equity and collateral
- Other bank report
- Manager’s opinion
Credit Report Analysis:
An analytical study is required whether a particular project is accepted or rejected:
- Managerial Aspect
- Organizational Aspect
- Technical Aspect
- Marketing Aspect
- Financial Aspect
- Economic Aspect
Selection of Borrowers: Selection of borrowers is to be considered as per lending principles and Bangladesh Bank Guidelines.
Borrower Selection Criteria: The following points should be taken into consideration:
- The borrower must be a real entrepreneur
- He must be resident of the project area
- He should have at least 20% of the total project value as his equity
- He should have the ability to offer collateral security acceptable to the lending bank
Methods of Selection:
In selecting the borrower, the following aspects should be considered
- Past behavior of the borrower requires to be studied. Enquiry should be made whether the applicant has availed of any loan previously from other bank and whether his dealings with that bank are regular or not.
- Work experiences of the intending borrower—what are the activities undertaken by him—his successes and failures along with analysis of the underlying factors.
- Whether the work area has any relevance to the project proposed to be undertaken y him.
On investigation and enquiry the banker reaches his conclusion to select a borrower that qualifies the 5(five) essentials, which may be termed as five C’s:
- Character
- Capacity
- Capital
- Condition
- Collateral
Character: Character denotes integrity of the borrower i.e. he should have willingness to repay the money borrowed. The banker should investigate every aspect of the character factor and should convince himself that despite adverse conditions, the applicant will make every effort to discharge his debt as per terms.
Capacity: Capacity means the ability to employ the funds profitably accordind to the terms and conditions. The capacity of the borrower has to be determined to find out his experiences in the line in which he is working.
Capital: Capital denotes financial soundness. The borrower must have his own stake in the business which creates a sense of involvement in the mind of the borrower. Capital is the financial strength of a risk as measured by the equity or net worth of the business.
Condition: Condition refers to the general business condition and the conditions in the particular industry in which the borrower is engaged. The banker should exercise prudence whether the business establishments are existent and continuing their business.
Collateral: Collateral implies the additional securities taken to offset weaknesses that are apparent. All of the collateral that may be made available to the bank will not make a bad loan good but it will make good loan better. While assessing valuation of collateral securities bankers need to take extra care by sampling survey and by examining information from land revenue office and also enquiring people nearby. The documents of the collateral securities are to be verified from the concerned Sub-Registered Office and other related office.
Over and above, we also stress on the following essentials:
|
5((five) Ps: |
5(five) Ms: |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
Types of Credit: Direct- indirect / Funded–Non-funded, Long Term-Short Term etc.
Depending on different criteria, nature & purpose, Loans & Advances may be categorized as follows:
On the Basis of Fund:
On the Basis of Duration:
- Long Term Credit
- Mid-Term Credit
- Short Term Credit
On the Basis of Security:
- Secured Advance
- Unsecured Advance
On the Basis of Size of Loan & Other Conditions:
- Retail Credit
- Corporate Credit
On the Basis of Sectors & Target group:
- Individual/Personal Credit
- Rural Credit
- Consumer Credit
- Micro Credit
On the Basis of Entrepreneurship:
- Small & Medium Enterprise
- Women Entrepreneurship
On the Basis of Participation & Risk Management:
- Syndicate Finance
- Consortium Finance
- Bridge Finance
In the Context of Foreign Trade:
- Import Finance : L/C, LIM, PAD, LTR
- Export Finance: ECC(H), ECC(P), BBLC
On the Basis of Loan Classification :
- Continuous Loan
- Demand Loan
- Term Loan
- Up to 5 years
- More than 5 years
- Short Term Loan
- Short Term Agricultural Loan (STAC)
- Micro Credit (MC)
In the Context of Foreign Trade:
- Import Finance : L/C, LIM, PAD, LTR
- Export Finance: ECC(H), ECC(P), BBLC
Comparative pricing of category wise deposit vs. advance / lending to maximize spread & allow mismatch beyond tolerable range:
Main Sources of Funds are:
- Deposits-
Customer or Household irrespective of Time and Demand Deposits
- Borrowings from other Banks and Financial Institutions-
Call, Placement, REPO, SWAP, Liquidity Support, Refinancing etc.
- Other Liabilities-
Various Payables & Adjusting Accounts Excluding Tax, VAT, Excise Duties i.e. all Government dues
- Capital/ Shareholders Equity-
Paid-up Capital, Reserves, Share Premium, Dividend and other Equalization Funds, Retained Earnings
Portfolio Management or Budgeting refers to diversification or distribution of assets to smother the inherit risks involve therein. The following is the main theme of portfolio management
“Don’t put all your eggs in one Basket”
Banks usually distribute their LDOs and Investments keeping the aforesaid into mind. Some sectors , shares or securities may get priorities but not the whole attention. However, the Mix or the Budget is formulated considering the following notable factors:
Factors to be considered for Portfolio Distribution
Among several factors some major factors are:
- Marketability
- Comparatively better Yield
- Environment and Climate Risk Aspects
- Govt. and Legal Aspects
- Risk Return Trade Off
Gap/Mismatch Risk:
- It arises on account of holding rate sensitive assets and liabilities with different principal amounts, maturity/re-pricing rates
- Even though maturity dates are same, if there is a mismatch between amount of assets and liabilities it causes interest rate risk and affects NII
IMPACT ON NII:
|
Gap |
Interest rate Change |
Impact on NII |
|
Positive |
Increases |
Positive |
|
Positive |
Decreases |
Negative |
|
Negative |
Increases |
Negative |
|
Negative |
Decreases |
Positive |






Appreciable article indeed!
Loans & Advances which is asset of a Bank should be sanctioned & disbursed on the basis of parties/borrowers integrity, efficiency,performances, net worth’s, clean CIB reports, business soundness etc.
Good article……………
in my entire life i have not seen such great site i am very satisfied from site and i have gotten a huge knowledge from this site i sulate to this website.
Onece again thank you so much sir
Nasar khan
MBA finance
pakistan
Thanks for posting such type of very go
od article. We would like to get this type of article more & more.
Dear sir,
I am 10% contribution in Pvt ltd company remaining 90 % others How much I am responsible for bank loan If the others director is not clear the bank loan. Company property mortgage by bank.
Proportionately